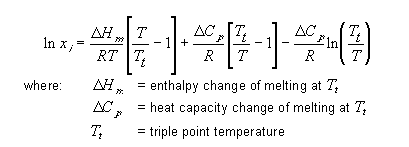
The vanít Hoff solubility method calculates solid-liquid equilibrium K-values for nearly ideal non-electrolyte systems. The solute and solvent should be of a similar chemical nature. The solubility of solute i at temperature T is given by:
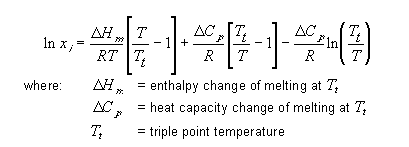
In practice, the melting temperature is usually used as this is easier to obtain than the triple temperature.
More information is available in the topic "van't Hoff Equation" under "Solid-Liquid Equilibria" in Chapter 2, Volume 1 of the PRO/II Reference Manual.
![]()
Related Topics
Thermodynamics - Technical Information
Solid Solubilities Constant Data
User-Supplied Solid Solubility Data
Fill Options for Solid Solubility Data