None |
No fill; all missing parameters are set to zero. |
UNIFAC |
The original UNIFAC method, where the van der Waals area and volume parameters are calculated from individual structural groups. It provides good order-of-magnitude estimates. |
Connectivity Index (CI) UNIFAC |
This is also called as CI UNIFAC, where the original UNIFAC method is used along with CI databank. The UNIFAC ”r;CI” bank is a self-contained VLE bank. Most of the VLE data in the UNIFAC ”r;SIMSCI” bank also shows up in the CI bank. This means the CI bank can be used standalone. In CI-UNIFAC fill option, main group interaction parameters data for UNIFAC structural groups is taken from CI bank and is used to calculate van der Waals area and volume parameters. The SIMSCI bank also contains LLE interaction data, but the CI bank does not contain LLE interaction data. |
Lyngby |
A modified version of UNIFAC that includes a three-parameter temperature-dependent form for the binary interaction parameter. In general, this generates better estimates than original UNIFAC. The keyword for this method is UFT1. The temperature-dependent portion of this method has the form:
|
Dortmund |
Another form of the UNIFAC method that employs a quadratic temperature-dependent equation. The temperature-dependent portion of this method has the form:
This generally is recognized as being developed more fully that the Lyngby form. The keyword for this method is UFT2. |
Regular Solution |
This fills missing parameters using the Regular Solution Theory developed by Hildebrand. It requires values for pressure, liquid molar volumes, and solubility parameters. It is suitable for nonpolar mixtures, but should not be used with highly non-ideal systems. Liquid molar volumes are measure at 1.0 atmosphere and 77F (25C). Users should be aware that this differs from standard liquid densities (or specific gravities) which are measured at (60F or 15.5556C). |
Flory-Huggins |
This method often is considered a correction to the Regular Solution Theory method. It considers the entropy effects of mixing molecules differing greatly in size. That make is suitable for polymer/solvent systems, especially when the molecules are non-polar. |
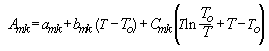 where To= 298.15K
where To= 298.15K